If you experience any issues, you can click here to submit a support ticket.
Free Training Videos
To access our Free Training Videos, use the password PDTR1234 when prompted.
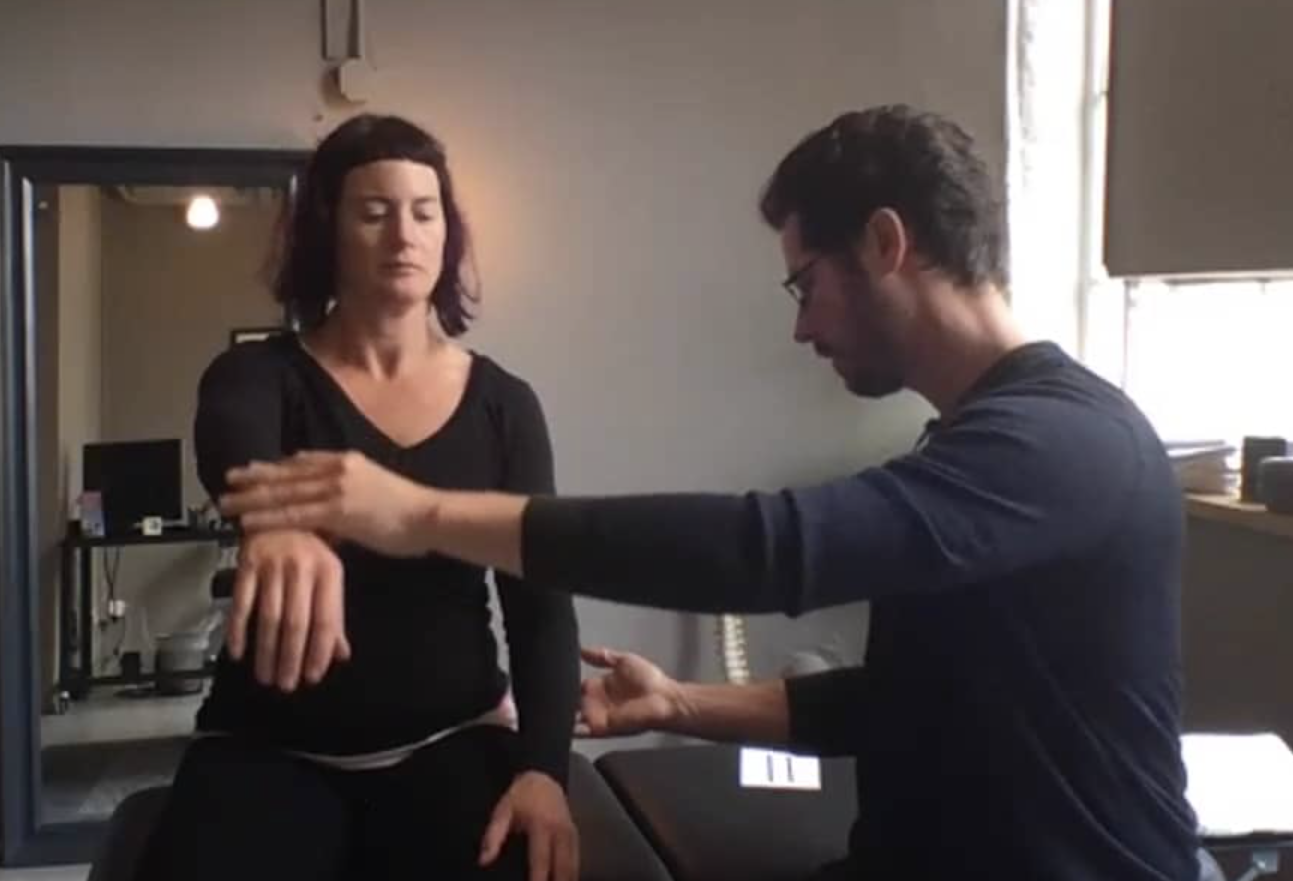
P-DTR Treatment Protocol Tutorial
Treatment Protocol:
- Direct muscle tests
- Indicator muscle tests
- UTL
- Double Stim & Double TL
- Using the rules of receptors to find the paired dysfunctional receptor
Advanced 1
 fail log in
fail log in 2017 London / Sydney Advanced Module 1
Pools / Pulls – 0:01:15
Basal ganglia – 0:20:45
Double UTL, spinal coupling – 0:42:11
Gastrointestinal sequence – 0:48:41
Ileocecal valve (ICV), acid reflux, GI reflexes, celiac desease – 0:53:15
Teeth & organs – 1:09:52
Baroreceptors – 1:16:09
Tongue – 1:24:50
Lymphatics – 1:31:09
Essential fatty acids (EFAs) – 1:33:35
Color sensitivity – 1:41:57
 fail log in
fail log in 2016 Oakland Advanced 1
Taste buds: bud to cranial nerve, bud to bud – 0:01:04
Lead-ins to organ dysfunction – 0:26:41
LKCs in tongue – 0:31:11
Lead-ins to tongue dysfunctions – 0:34:28
Tongue-hyoid pair – 0:36:50
Neck extensor hypertonicity – 0:45:47
Organ VRP & VPP cases: proper and anti-stim; using far/near focusing & jaw re/protrusion – 0:48:50
Visceral sequence – 1:06:55
Nutrients: ETC / Krebs Cycle & EFAs – 1:16:45
Lethargy, low energy; common adrenals pairing – 1:31:10
EFA metabolism – 1:32:45
Organ dysfunctions post-treatment – 1:42:45
Treatment plan for nutrients – 1:48:40
Testing for food intolerance vs allergies – 1:50:11
 fail log in
fail log in 2016 London Advanced Module 1 (Aug-Dec)
Organ, tongue dysfunctions incl. Brain; using jaw protrusion – 0:01:04
LKC of tongue (effect on hyoid) vs. VRP – 0:16:30
Taste receptors vs. mechano-stims on tongue – 0:31:07
Food sensitivities – 0:34:38
Hyoid vs. tongue/eyes vs. TMJ – 0:39:04
Crude touch vs. parasympathetic stim – 0:41:44
Acid reflux approach – 0:47:16
Mesentery dysfunction – 0:49:38
Acid / alkaline dysfunction: hypothalamus, pituitary, stomach – 0:54:05
Trigger vs. dysfunctional receptor – 0:55:10
Priority emotion coming back – 0:58:11
Trigger causing multiple priority dysfunctions – 1:02:46
Excessive sympathetic symptoms, constipation – 1:04:02
Throat tension during swallowing – 1:07:56
Lead-ins to tongue: TMJ, swallowing, foods, headaches, tongue movement… – 1:09:12
Food intolerance vs. sensitivity – 1:10:49
Insomnia – 1:13:45
Organs: no change after treatment – 1:15:46
Helicobacter / H. Pylori infection & organs – 1:15:46
Advanced 2
 fail log in
fail log in 2018 San Francisco Advanced Modules 1 & 2
-Tongue
-Organs
-ICV syndrome
-Alkalosis
-Retrograde lymphatics
-Baroreceptors
-EFA metabolism
-Krebs cycle
-Cranial nerves
-Neurological tooth
-Referred tooth pain
-Primitive reflexes
-Peripheral nerves
-Pools
 fail log in
fail log in 2018 Berkeley Advanced Webcast Module 1 & 2
Nerve entrapment upper extremity, use of d-UTL, use of X lines for mechano-receptors – 0:00:28
Lumbar spine & lower extremity case – nociceptor & mechano-receptor – 0:24:28
Checking for pools – 0:42:53
Use of X lines for mechanoreceptor-caused dysfunctions – 0:45:10
Primitive reflexes: startle, palmr grasp, tonic labyrinthe, symmetrical tonic, asymmetrical tonic, morrow & fear paralysis, – 0:46:25
Cranial nerves: lead-ins, P vs. S vs. T; assessment, breathing patterns, case of i, ii, v, vii and viii – 1:00:06
Constipation & digestive issues – 1:31:23
Digestive sequence – 1:33:26
VPP/VRP of organs; dysfunction with pool – 1:38:11
Basal ganglia – 1:51:00
Lymphatic Retrograde – 1:55:34
Surrogate testing – 1:59:09
 fail log in
fail log in 2017 London Sydney Poland Advanced Module 2
Cranial Nerves: testing overview – 0:01:30
Cranial Nerves: pairing – 0:20:40
Primitive reflexes: Palmar grasp, Righting, Moro, STNR, ATNR – 0:27:09
Primitive reflexes: treatment & use of double UTL – 0:36:06
Krebs Cycle: test – 0:42:26
EFA metabolism: aspirin test – 0:44:39
Krebs Cycle & ETC: nutrient testing – 0:45:26
EFA metabolism: nutrient testing – 0:51:15
Cranial faults & organs for nutrient absorption – 0:52:06
Tongue receptors – 0:56:46
Lymphatic Retrograde & switching due to organ – 0:57:22
Nerve entrapment testing – 1:06:40
 fail log in
fail log in 2017 Oakland Advanced Module 2
Cranial Nerves: basic mode – 0:01:13
Best frequency for CN viii Vestibulocochlear – 0:04:20
CN-CN pair topped by nociception: assessment, pairing and treatment – 0:04:42
Finding a receptor paired with Cranial Nerve – 0:24:33
Tongue receptor – 0:26:24
When to take P Cranial Nerve to basic mode – 0:30:00
Cranial Nerves: Triple stim demo – 0:30:47
Priority between Cranial Nerves using secondaries – 0:34:42
Cranial Nerves vs. spinotectal visual and audio; CNs with identical stims – 0:42:34
Cranial Nerves: choosing between different breathing patterns – 0:46:26
Cranial Nerves: using eye systems & simultaneous stims of L and R eye – 0:46:50
Lead-ins to Cranial Nerves – 0:49:02
Cranial Nerves: eye systems in different CNs – 0:52:10
Cranial Nerves: lead-ins – 0:54:28
Dysfunctions negated by stim to CN – 0:57:41
Role of tertiaries in CN dysfunctions – 0:58:36
Trans-neural degeneration – 1:08:28
Cranial Nerves: breathing patterns – 1:13:42
Cranial Nerves: approaching two priority Ps – 1:16:55
Cranial Nerve sequences – 1:17:57
Cranial Nerves vs. aerobic / anaerobic dysfunction – 1:19:07
Cranial Nerves: testing speech phonation (CN 9 & 10) – 1:20:18
Cranial Nerves: sequences demo – 1:21:03
Nerve entrapment: arm, shoulder, neck – 1:23:50
Nerve entrapment: putting individual nerves in tension, review of major nerve paths, general approach – 1:41:10
Nerve entrapment at lower extremity – 1:50:00
Primitive reflexes: – 1:57:10
 fail log in
fail log in 2016 Oakland Advanced Module 2
Cranial Nerves: breathing patterns – 0:00:46
Cranial Nerves: stimulation – 0:05:00
Cranial Nerves: common pairs – 0:22:10
Cranial Nerves: rules – 0:23:26
Cranial Nerves: protocol – 0:26:08
Cranial Nerves: Tertiary rules – 0:36:54
Primitive reflex dysfunction topped by nociception, topped by cranial nerve – 0:41:57
Cranial Nerves: treatment & priority – 0:51:13
Startle reflex: visual vs. auditory (Moro reflex) – 0:59:15
Clinical tips: visual, testing, history – 1:02:10
Cranial Nerves: priority, receptor to cranial nerve – 1:08:20
 fail log in
fail log in 2016 London Advanced Module 2 (Aug-Dec)
Brain nuclei lead-ins – 0:00:25
Prioritizing dysfunctions – 0:03:20
Cranial nerves – 0:05:00
Brain nuclei sequence – 0:32:49
Determining priority – 0:34:37
Brain nuclei vs. sympathetic/parasympathetic pathways – 0:44:05
Brain nuclei pairing – 0:46:05
Cranial Nerve 2 – 0:47:37
Cranial Nerve 2 & 3 – 0:49:45
Convergence, seccades & VOR – 0:50:58
Lead-ins to priority – 0:52:43
Brain nuclei pairing – 0:56:42
Use of tertiary with Brain Nuclei – 0:59:09
Cranial Nerve 12 – 1:05:49
Lazy eye – 1:06:23
Cranial Nerve 10, Vagus – 1:07:05
Normal position of tongue – 1:09:25
Eyes: far-sightedness – 1:11:22
Cranial Nerve 8 & 2; use of tertiary – 1:12:10
Chemical reaction – 1:22:50
Cranial Nerve 7, Facial, and 5, Trigeminal – 1:23:27
Basic
 fail log in
fail log in P-DTR Muscle Testing Video
Foundation 3 Day 1
 fail log in
fail log in 2017 DC Foundations Module 1
How to deal with hypertonicity? Food, valsalva, emotions – 0:00:25
Switching – 0:12:58
Understanding importance of modes of dysfunction; dealing with hyper modes – 0:14:47
Event: case, importance of eye position – 0:26:52
Navigating through finding the pair, using UTL, history, visual assessment – 0:43:00
Landing on a Secondary first – 0:52:53
Inability to get a reflex – 1:01:22
Role of TL in live case, finding secondary – 1:03:48
Rules of TL chart – 1:13:50
Strong muscles, but painful connective tissue after treatment – 1:19:05
 fail log in
fail log in 2017 Vancouver Module 1 Foundations
Bag-chain dysfunction recurrence – 0:00:16
Autogenic responses, switching, emotions – 0:04:30
Bag-chain dysfunction demo – 0:07:46
Entry points to a dysfunction: landing on tertiary – 0:14:10
TL flipping results – 0:26:14
Entry points to a dysfunction: landing on secondary – 0:28:19
Use of opposite stim – 0:31:37
Local switching lead-ins – 0:43:33
Rule of “TL flips” – 0:52:41
Timing of stim and IM test – 0:54:19
UTL vs. local TL use – 0:54:54
Reactor-reactive (R&R) – 0:59:15
Multiple dysfunctions in same muscle – 1:01:32
Explaining hypertonicity & switching to clients – 1:07:07
Double-stim vs double-TL, TL vs. UTL, TL vs. a muscle test – 1:11:47
Global hypertonicity & switching treatment – 1:22:03
Starting with strong-in-the-clear muscle – 1:26:55
Event – 1:29:33
Low back pain approach – 1:36:10
Global weakness – 1:39:06
Muscle tests for whip-lash – 1:40:23
 fail log in
fail log in 2015 Oakland Module 1 Basic
Dysfunctional receptor effect on multiple muscles or the same muscles in multiple patterns; how to screen – 0:00:56
Starting with strong-in-the-clear muscle – 0:07:38
Starting with weak-in-the-clear muscle; landing on a Tertiary first – 0:10:01
Entry protocol recap – 0:17:21
Wrist U-TL – 0:18:38
R&R primary & secondary – 0:19:50
Natural flow: shoulder case – 0:21:52
Approaching hypertonic muscles – 0:32:10
Hyper 3 & 4 modes: when a receptor has TL – 0:40:40
Chemoreceptors – 0:42:23
Mechano-receptors – 0:44:05
Various tests for Transverse Abdominus – 0:45:27
Is it important to know the exact mode of dysfunction? – 0:48:57
Challenging the corrections – 0:53:21
TL-hunting, homework, manual release use – 0:54:53
Approach to lower back pain: erectors, abdominals, pelvic floor – 1:01:50
Scars – 1:06:04
Tattoos – 1:07:37
Natural flow treatment: visual assessment, palpation, muscle testing, strategies on finding the pair – 1:10:20
 fail log in
fail log in 2016 Denver Module 1 Basic
Entry points, nuclear bag & chain example – 0:02:50
Related muscles – 0:22:53
Switching, hypertonicity – 0:27:27
Reactor-reactive; modes of dysfunction – 0:33:50
Hypertonicity – 0:44:21
UTL – 0:50:00
Indicator muscles and tendons for elderly – 0:52:12
restless leg – 0:54:26
leg cramps – 0:54:58
Sciatic/other nerve pain – 0:55:50
Double-TL vs. double-stim – 1:00:25
Hypertonicity – 1:04:15
visual lead-ins for primaries and secondaries – 1:09:09
 fail log in
fail log in 2016 Phoenix Module 1 Basic
Rules for primary & secondary: IM + various TL/double-TL + various stim/opp-stim/anti-stim – 0:03:51
Difference in use of local TL vs. Universal TL – 0:18:20
Jaw: muscles, hypertonicity, clenching, mechanoreceptors – 0:21:42
Hyper 4 and 5 modes of dysfunction – 0:31:27
Reactor-Reactive (R&R) review; abdominals to erectors relationship; relief in pain – 0:40:06
Landing on a Tertiary – 0:46:15
How to approach hypertonicity – 0:57:24
Options for DTR – 1:04:30
Foundation 3 Day 2
 fail log in
fail log in 2017 DC Foundations Module 2
2:50 – Treatment Flow
5:00 – History
7:00 – Active ROM, reasons why patients will change movement pattern
10:30 – Testing Passive ROM with and without additional assisted motion
12:00 – Dealing with local hypertonicity; Testing for Pattern of Inhibition & Hypertonicity
15:00 – Mode of dysfunction
17:15 – Using X lines to determine if weakness is from Mechanoreceptor or Nociceptor
19:00 – CC ligament related to humeral depressors
22:00 – Explanation: Pairing Stim to determine Golgi – Golgi vs Golgi – Pacini
27:45 – Using the Nose or ear to cause inhibition
30:00 – Pacini – Golgi Dysfunction
35:00 – Testing yourself for switching (*note: not completely reliable but it can help to know)
38:00 – All Multi Dysfunction & Discussion of Hyper 3+ & Protocols
49:30 – Impact Paleo causing hypertonicity of B-middle scalenes
51:00 – How to Find Secondary Neo from Impact Paleo in Spine
55:00 – Testing for Multiple Vectors of Impact Paleo – How to know which one to treat
59:30 – Talus: Looking for a Pattern of Inhibition
1:04:15 – Protocol: Using a Secondary to find the Primary
1:07:40 – Rules of Nose & Earlobes
1:13:35 – Review of Spinal Ligaments & Tx
1:22:50 – Pelvic Categories & Relationship with Impact Paleo
1:31:00 – Using the Rules to Determine What to Treat
1:33:45 – Discussion & Overview of Neurogait 2
 fail log in
fail log in 2017 Vancouver Foundations Module 2
Normal vs dysfunctional neos – 0:00:39
Spinal ligaments: ALL, PLL, sperspinous, intraspinous; all-multi example; scoliosis – 0:13:37
Disk herniations – 0:29:53
All hyper-multi dysfunctino level – 0:31:35
Hyper-3 to hyper-5 mode and double-TL – 0:32:47
Light-headedness after treatment – 0:37:47
Reactor-reactive (R&R) – 0:40:00
Impact paleo in the spine: lead-ins & case, differentiating spine segments – 0:46:29
Flow: spinal ligament treatment – 0:53:30
PMRF presentation and anti-stim – 0:56:20
Tension in ligaments, hyper-reactive/-reflexive golgis – 0:59:03
Thalamic inhibition pattern – 0:59:44
Reactor-reactive (R&R) – 1:00:04
Modes of dysfunction: case flow, local switching – 1:04:53
Flipping effect of TL through the modes of dysfunction: natural flow pacini-vibration case – 1:18:10
Nerve entrapment at shoulder-neck – 1:31:50
 fail log in
fail log in Denver Module 2 Basic 2016
Golgi and pacini dysfunctions: client assessment & approach – 0:00:20
Golgi-pacini best practices & pitfalls – 0:22:13
Client TL vs UTL – 0:28:40
UTL vs. local TL – 0:30:47
PMRF presentation – 0:35:20
Difficult receptor locations – 0:49:56
Knee assessment & impact paleo case – 0:53:22
Nociceptive withdrawal & PMRF presentation – 1:06:40
Finding a main S – 1:10:37
TS line – 1:16:37
Joint capsule golgis – 1:23:47
 fail log in
fail log in 2016 Phoenix Module 2 Basic
Finding the P of a secondary; finding the S to a primary – 0:01:10
Hypertonicity – 0:14:38
Visual evaluation of dysfunctions – 0:20:02
Multiple dysfunctions influencing a muscle – 0:22:45
Neo-paleo in pelvic floor – 0:27:32
Receptor pairings – 0:33:20
Hypertonicity – 0:36:51
Common ligament pairings – 0:39:42
Late toe strike in gait; foot dysfunctions – 0:48:06
UTL makes client weak – 0:58:11
Scars – 1:01:05
Spine ligaments – 1:07:50
Golgi stim vs. bag fiber stim – 1:11:45
Hypertonicity – 1:14:27
 fail log in
fail log in 2015 Oakland Module 2 Basic
Anterior & Posterior Longitudinal ligaments and spinal ligament protocols – 0:00:40
Rules: effect of stim on main secondary – 0:21:16
Double-stim demo for all receptors – 0:29:07
Jolt paleo in arm, leg and cervical spine – 0:37:05
Nociceptor vs. mechanoreceptor perception in the brain – 1:02:25
Neo pairing – 1:09:35
Golgis, pacinis and UTL – 1:11:18
Reactor-reactive (R&R) – 1:17:48
Golgi/pacini pairing: timing, execution; tapping vs. stretch – 1:22:30
TL secondary to find primary and vice versa – 1:34:52
Visual scanning for patterns – 1:43:43
Finding secondary neo – 2:01:05
Multiple dysfunctions in a muscle – 2:03:45
Increase in pain from clearing golgis – 2:05:13
Receptors in eye muscles – 2:06:40
Foundation 3 Day 3
 fail log in
fail log in 2017 Vancouver Foundations Module 3
Dissecting an upper extremity case: shoulder complex & forearm muscle testing; pacini-vibration pair – 0:00:33
Approaching hypertonic muscles – 0:13:47
Rules of cartilage & practical application – 0:21:22
Hypertonicity case: id’ing responsible P, id’ing related S; challenging results; jolt paleo, pacini-golgi, bag-chain; vibration-pacini – 0:25:57
Indicator Muscles in different positions – 0:37:30
Pelvic categories & jolt paleo: switching, finding priority, challenging the correction – 0:44:43
Pelvic category 3: proper stim; joint capsule rules – 0:54:37
Joint position sense: conscious vs. unconscious; where to look for golgis; case of shoulder, neck & jaw – 1:01:28
DTR options – 1:13:48
 fail log in
fail log in 2015 Oakland Module 3 Basic
Ilio-lumbar ligament in gait; frozen gait – 0:01:02
Supine gait testing; PALO-ALTO – 0:10:58
Pelvic Categories – 0:19:14
Pelvic Category 2 & breathing (diaphragm/abdominals & cranium) – 1:05:20
Talus & neurogait – 1:16:45
Gait in prone – 1:30:15
Piriformis testing – 1:31:48
PALO-ALTO stimuli – 1:34:38
Sacrospinous ligament palpation – 1:36:40
PiLUS, gait & pelvis – 1:38:18
joint capsule golgis – 1:42:50
Clinical presentation of receptors – 1:49:00
External rotators tests – 1:53:30
Clinical presentation: tenderness & soreness – 1:55:33
Pairing pacinis and golgis – 1:56:56
 fail log in
fail log in 2016 Phoenix Module 3 Basic
UTL or TL use – 0:01:40
Double stimulus – 0:08:50
Vibration receptors – 0:15:20
Pelvic Categories – 0:26:27
Global weakness, hypotonicity – 0:59:50
Pelvic Category 3 – 1:02:40
Anterior and Posterior Longitudinal ligaments – 1:05:08
Anterior inferior sacral ilio-lumbar ligament; Frozen Gait – 1:09:55
Finding the P of a secondary – 1:15:22
Finding the secondary of an impact paleo P – 1:19:27
Foundation 3 Day 4
 fail log in
fail log in 2018 San Francisco Foundations Module 4
Vertebral Fixations – 0:01:43
Limbic Fixation – 0:14:31
Hypo ligaments – 0:16:24
Palpation of vertebral fixations – 0:24:45
Posterior rib fixation in mid-Thoracic – 0:31:15
Meridians – 0:37:45
Cranial faults – 0:49:20
Emotions: psychological reversal – 1:15:48
Emotions – 1:20:01
 fail log in
fail log in 2015 Oakland Module 4 Basic
Lead-ins for crude touch – 0:01:00
Joint position dysfunction – 0:03:25
Using eyes for joint position dysfunction – 0:08:27
Spine and joint position dysfunction. – 0:09:39
Eye dysfunctions and joint position dysfunction. – 0:14:42
Lead-ins to joint position dysfunction – 0:15:35
Joint position dysfunction and spinal ligaments – 0:17:09
Distal joint dysfunctions superior to pelvic categories – 0:18:00
Symptoms and pitfalls of cloacals – 0:20:46
Secondary crude touch and a secondary fine touch. – 0:41:57
Crude touch to paleo pairing, common pitfalls – 0:56:10
Proper stim for fine/crude touch, tickle, itche, hot and cold receptors – 1:04:36
Tickle-itch dysfunction demo – 1:08:25
Hot-cold dysfunction demo – 1:12:50
Adrenals, Monotasking – 1:20:53
LKC – 1:37:22
Differentiating lead-ins between cloacals and PALO-AK – 1:41:02
Eye lead-in for adrenals vs. eye dysfunctions – 1:43:10
Use of DHEA for adrenal issues – 1:47:50
Foundation 3 Day 5
 fail log in
fail log in 2016 Denver Foundations Module 5
Monotasking + Emotions – 0:00:16
Long, short & closed LKCs – 0:13:38
LKCs in hierarchical sense – 0:28:38
LKCs & cranial faults – 0:29:53
Cranial faults – 0:31:12
Adrenals – 0:52:05
Spinal fixations – 0:56:50
Ileocecal valve (ICV) – 1:00:00
Meridians – 1:03:47
Pairs with paleo – 1:09:00
Secondary emotions – 1:10:23
Nociceptors and use of UTL – 1:12:22
 fail log in
fail log in 2015 Oakland Module 5 Basic
Finding P neo to a jolt paleo S – 0:00:33
Using UTL and anti-stim with S nociceptor – 0:05:32
Finding P pacini to a vibration mS – 0:09:33
ID’ing meridian dysfunctions – 0:13:10
Spinal fixation: weakness & hypertonicity – 0:19:47
Efficiency in pairing to paleo – 0:24:30
Pelvic floor in context of cranial faults, meridians – 0:25:54
Emotions – 0:31:28
Neurologic tooth – 0:37:35
Meridians and indicator muscles – 0:45:00
EmotionsCranial sutures involved with ilio-cecal valve (ICV) – 0:54:18
Sacral faults – 1:04:57
Spinotectal, spinomesencephalic – 1:17:57
Sacral fault stimuli – 1:25:28
Spinotectal as tertiary in crude-fine touch dysfunction – 1:30:24
Concussions – 1:40:00
Proper location of pairing stimulus – 1:48:31
Proper Nasosphenoid Cranial Fault stimulus – 1:49:40
Reactor-reactive supercedes meridian – 1:50:19
TS line – 1:56:47
Spinotectal receptors in use for pelvic floor -2:00:52
Foundation 4 Day 1
 fail log in
fail log in 2018 Poland / San Francisco Foundations Module 1
Rules of receptors
Rules of TL
Proper stimulation and proper double stimulus
Protocols to find paired receptors
Switching and Hypertonicity
Nuclear chain fibers / Nuclear bag fiber dysfunctions
Neospinothalamic / Paleospinothalamic (Spinoreticular)
Impact Paleo dysfunctions
 fail log in
fail log in 2017 Calgary Foundations Module 1
(1) can you show muscle testing positions for abdominals, erector spinae, SCM vs scalenes, base of occiput muscles
2) does a person need to have sensation in a scar in order to effectively do a neo stim (as part of assessment or treatment)?
3) can you show landing on a tertiary first and how to find a secondary or primary from it.
4) can you demonstrate question #3 from the last quiz?
5) can you please give more ideas of what to look for with observations /gait
6) Can you demonstrate working through an inhibition pattern (NWR, PMRF, extrapyramidal or thalamic inhibition pattern)?
7)Is there any time when you would not do PDTR on someone (I’m thinking when something is acute perhaps) Any other time?
8) how do you approach pelvic floor dysfunctions? ie. how do you apply stims / anti-stims etc
9) if doing PDTR on a pregnant woman, can the baby interfere with getting an accurate reading of things?
10) can you demo neo / paleo of the head
11) assuming multiple dysfunctions can exist in the same area, how does that look and what’s the approach for treatment?
12) where do you start with people coming in with headaches as main complaint? Test neck musculature and then potentially anti-stim head?
13) do you ever need to test eye muscles and respiratory muscles? If so, how?
14) will eye position affect neck muscle testing?
 fail log in
fail log in 2017 Denver Foundations Module 1
Injured shoulder case: testing autogenic response, history, shoulder girdle muscle testing; mode of dysfunction (hyper multi 4); finding a S neo to jolt paleo P; challenging the work – 0:01:25
Options for indicator muscles in prone – 0:15:33
Low back pain case: muscle testing; PMRF inhibition pattern – 0:20:38
Jolt paleo case: visual assessment; proper muscle testing; mode of dysfunction; finding secondary neo – 0:29:20
Proper way to double-stim mechano- and nociceptors – 0:45:43
Reactor-Reactive (R&R): palpation, moes of dysfunction, related muscles; treatment – 0:54:15
Bag-chain case: mode of dysfunction, landing on a virtual S first and finding the P and main S; – 1:04:30
Global hypertonicity: causes & approach – 1:09:27
Practitioner hypertonicity – 1:13:23
 fail log in
fail log in Oakland Module 1 Basic 2017
Workflow on patient with complaint, integrating P-DTR into your practice – 0:00:34
Case, patient workflow: assessment, muscle testing, direct muscle testing vs. indicator – 0:05:49
Nociception case: visual assessment, inhibition pattern; muscle testing; finding the main S – 0:21:20
Mechanoreceptor case: rules of U-TL vs. TL, rules of P and S, – 0:38:18
Global hypertonicity vs. global weakness – 0:45:33
Use of local TL & double TL – 0:49:31
Neurological effect of d-TL; use of anti-stim – 0:55:18
Palpating dysfunctional receptors; landing on a virtual S, landing on a P – 0:57:34
Lead-ins to R&R – 1:05:28
Zooming in on the receptor area with anti-stim – 1:13:04
Use of virtuals – 1:14:02
Importance of modes of dysfunction – 1:15:44
Muscle test for neck & levator scapulae – 1:19:34
 fail log in
fail log in 2016 London Module 1 Basic
Hypertonicity: global vs. local; modes of dysfunction – 0:02:20
Key concepts for the beginner: muscle testing, history & visual observation; case; pitfalls – 0:12:05
Multiple dysfunctions affecting the same muscle – 0:24:56
Use of Tertiary muscles – 0:28:09
Reactor-Reactive (R&R): tid-bits, lead-ins, treatment options – 0:31:16
Bullet-proofing your work – 0:36:48
Receptor Rules – 0:39:55
Approaches to finding Primary – 0:50:22
Jolt paleo as P and as S: rules – 0:57:52
Jolt paleos in spine; rules for nociceptos; ruling out mechano-receptors – 1:02:41
Hierarchy on receptor importance – 1:09:56
Stim to deep muscles: psoas – 1:11:42
Starting with strong muscles – 1:23:54
Reactor-Reactive (R&R): palpatory & visual assessment, using the Reactive; shoulder & neck case – 1:28:35
 fail log in
fail log in 2016 London Module 1 Basic (Aug-Dec)
Use of U-TL vs. local TL – 0:00:41
Use of U-TL & local TL with proper and opposite stim for mechano- and nociceptors – 0:06:16
Need for muscle testing – 0:17:34
Receptors found in scars – 0:19:05
Need to stim the inhibition pattern: modes of dysfunction; bullet-proofing the work – 0:20:02
Neo & paleo: inhibition patterns – 0:25:52
Core muscle testing: Rec Ab, Obliques, TVA, Rotatores/Multifidi – 0:33:45
Weak Transverse Abdominus – 0:43:40
Spinal extensor muscle testing – 0:46:52
Receptors in joint: jolt paleo to neo; ways to find the pair – 0:48:51
Hypertonic muscle case – 0:57:39
Flipping effect of TL on receptors & muscles in different modes – 1:06:20
Weak muscles and Reactor-Reactive (R&R); rules of Tertiary – 1:16:07
Impact paleo in spine – 1:21:10
Stim to joint vs. stim to skin around joint; hierarchy – 1:27:30
Impact paleos in joints: shoulder, hip, jaw, pelvis – 1:29:30
How much correction in one session – 1:34:58
Causing global hypertonicity from treatment & approach to client history – 1:35:56
Practitioner hypertonicity – 1:41:56
Eye muscles – 1:43:12
Effect of breathing on results – 1:44:02
When corrections come back – 1:46:29
Difficult globally hypertonic cases – 1:49:01
What causes muscle testing to change without stim – 1:51:57
Testing extraocular muscles – 1:55:23
 fail log in
fail log in 2015 London Module 1 Basic
Reactor-Reactive (R&R): presentation, lead-ins, effect on symptoms, options for clearing – 0:00:51
Finding Neo receptors as secondary and as primary: visual assessment, inhibition patterns; Hyper 4 case – 0:08:22
Visual lead-ins to mechano-receptors – 0:24:54
R&R: looking for the reactive muscle; core muscles & low back pain; compared to bag-chain example – 0:32:40
Causes for & mechanism of dysfunctional receptors – 0:37:50
Approach to patient complaints in clinic – 0:40:30
Palpation lead-ins to dysfunctional receptors – 0:42:33
How to approach persisting pain symptoms – 0:48:08
Diabetic poly-neuropathy – 0:53:36
Multiple dysfunctions in same muscle – 0:54:35
Dysfunctions & low back pain: muscle testing; knee jolt paleo hyper mode – 1:01:27
Receptors in deep compartment muscles: example of psoas affected by paleo-neo pair – 1:10:41
Dealing with structural and hardware problems; sciatica – 1:18:40
Approach to global inhibition – 1:21:46
Approach to hypertonicity: CNS strategy, symptoms, example of local – 1:23:51
Global hypertonicity: causes & approach – 1:29:55
Difficult to reach scars & nociceptors – 1:31:41
Bilateral weakness in muscles: reasons – 1:34:37
Screening for dysfunctions affecting a muscle – 1:37:12
Options for DTR; hyper-reflexia – 1:40:13
Pelvic floor: muscle testing, choice of IM, TL, case of neo primary to paleo secondary – 1:43:36
Foundation 4 Day 2
 fail log in
fail log in 2019 SF Module 1 & 2 Foundations Review Webinar
Review of Foundations module 1 & 2 with a live model. Send in questions or ask questions live. Watch live and review after with recorded video.
Topics:
Rules of P-DTR
Rules of TL & UTL
How to treat Hypertonicity and Switching
Protocols
Seeing dysfunctions
Pairing stims
Related muscles
Nociceptive Withdrawal Reflex
PMRF pattern
Golgi, Pacini, Vibration
TS line
The Event
 fail log in
fail log in 2017 Oakland / Sydney Foundation Module 2
Normal autogenic response and use of cartilage – 0:01:10
Ankle case with golgis – 0:04:45
Normal session flow. Low back pain – 0:09:20
Strategy in addressing golgis; impact paleo – 0:15:43
Ligaments of the spine – 0:22:43
PiLUS – 0:32:54
Gait inhibition, frozen gait – 0:39:54
Pelvic Categories – 0:44:41
Hypertonicity – 0:46:44
Greater trochanter, hip pain – 0:53:36
PALO-ALTO – 0:55:25
Sacral distortion – 1:00:09
Neurogait: proximal transverse ligament – 1:01:04
Neurogait: talus – 1:02:04
Muscle testing – 1:04:26
Neurogait: talus – 1:07:30
Inguinal ligament & hernia – 1:09:48
 fail log in
fail log in 2016 London Foundation Module 2 (Aug-Dec)
Proximal & distal transverse ligament of foot: stim, inhibition patterns, case; Strategies to find P from virtual S and main S from P; Joint capsule vs. non-joint capsule golgi – 0:00:40
Spinal ligaments (location, proper stim); vertebral gliding – 0:15:31
Ilio-lumbar ligament: anatomy & proper stim for superior, inferior and anterior bands, gait – 0:23:20
Double-stim for ligaments of the spine; case using TS line – 0:26:40
Sacral distortion: stim, double-stim, case – 0:33:40
Gait dysfunctions: lead-ins & presentation, assessment, case – 0:43:25
Rules of pairing receptors – 0:54:02
Anti-stim for nociceptors vs. proper stim for pacini – 0:55:41
Event: procedure, proper position – 1:01:15
Talus displacement: visual assessment, muscle testing, case – 1:07:36
Hyoid: normal response, dysfunctions, inhibition patterns, – 1:16:58
Rules of earlobes & nasal cartilage; case; focal switching; importance of modes of dysfunction – 1:21:54
Joint capsule vs. non-joint capsule – 1:30:11
Neo-impact paleo pairs on hip & shoulder: how to find P or S – 1:36:30
Lower back pain & pelvic categories – 1:46:22
Shoulder case in slow motion: history, assessment, muscle testing, pairing, treatment – 1:49:00
 fail log in
fail log in 2015 Sydney Module 2 Basic
How to start in session – 0:03:13
Manganese for ligaments – 0:14:40
TL weakens strong muscles – 0:17:09
TL strengthens weak muscles – 0:22:42
Withdrawal patterns – 0:32:52
Cartilage inhibition responses – 0:41:00
PALO-ALTO – 0:46:36
Golgi, pacini and vibration hunting & pairing – 0:54:02
Pelvic Category 1 – 1:05:22
Pelvic Category 3 – 1:17:30
Intrinsic muscle tests – 1:24:52
PLUS / PiLUS – 1:30:16
Modes of dysfunction use – 1:34:34
PMRF, hemisensory, thalamic patterns – 1:36:05
Pelvic Category 3 vs. supraspinous & ileo-lumbar ligaments – 1:36:55
Psoas reasons for weakness – 1:47:20
Anterior & posterior longitudinal ligaments assessment & treatment – 1:48:43
Anterior hip pain case approach – 1:59:13
Approach to hardware issues – 2:02:17
 fail log in
fail log in 2016 London Foundation Module 2
TS line diagnosis & treatment: finding a dysfunction via the TS line – 0:00:12
Bullet-proofing the receptor pair: nociception, golgi-pacini – 0:07:26
Ligament rules & muscle inhibition – 0:17:47
High pay-off golgi areas – 0:23:05
Pelvic Categories: lead-ins, symptoms, entry, muscle testing, effect of impact paleos, overlapping dysfunctions – 0:25:41
Hyoid for diagnosis & treatment: inhibition patterns, muscle testing, normal response, – 0:51:12
Frequency in pelvic categories – 0:54:19
PALO-ALTO: theory, testing – 0:55:28
Ligaments of the spine (ALL, PLL, supraspinous, inter-transverse, inter-spinous): inhibition, muscle testing, normal response – 0:59:45
Addressing gait issues: motion assessment & history, case of hip jolt paleo – 1:06:33
 fail log in
fail log in 2015 London Module 2 Basic
Prioritization at Fundamentals level – 0:00:32
Shoulder ROM & Vibration – 0:04:09
Testing non-joint ligaments of spine; Anterior Longitudinal ligament – 0:12:00
Pelvic Categories – 0:21:06
Scars – 1:08:36
PALO-ALTO – 1:21:56
PLUS / PiLUS – 1:31:07
Talus – 1:38:31
Cartilage inhibition responses – 1:43:40
Foundation 4 Day 3
 fail log in
fail log in 2017 Oakland / Sydney Foundations Module 3
Review of Fundamentals Quiz – 0:01:10
Identifying the right receptor after an anti-stim (crude touch to fine touch) – 0:08:05
Demo of receptors and their inhibition patterns: NAR, PMRF, NWR – 0:14:11
Why primary & secondary receptors are generally not in their related muscles – 0:25:37
Cloacal synchronization; determining priority – 0:27:46
Long Kinematic Chains (LKCs): long, short, closed and hidden – 0:36:50
Joint position sense co-mingled with closed LKC: patellar reflex normalizing bilaterally from two closed LKC corrections – 0:47:15
Nerve ending for spinomesencephalic receptor – 0:57:00
Reducing acute pain with spinomesencephalic – 0:58:50
Spinothalamic pathways (spino-mesencephali, spinohypothalamic, hot: lead-ins, assessment, treatment – 0:59:35
Spinotectal response and uses: functional, dysfunctional – 1:08:42
Spinomesencephalic: experimenting with anti-stim – 1:12:47
Spinotectal audio to paleo pair, inhibition pattern, pitfalls – 1:13:58
Joint Position Sense: shoulder example – 1:19:03
Joint Position Sense: spine example causing spinal fixation – 1:22:45
Limbic fixation: nature, related muscles, lead-ins – 1:27:00
Iliac fixation – 1:28:56
Spinal fixations: lead-ins – 1:30:23
Adrenal Protocol: weak or hypertonic related muscles; focal switching – 1:31:32
Conscious/unconscious vs. spinomesencephalic – 1:42:33
IM options for pelvic category dysfunctions – 1:43:02
Cold dysfunction case – 1:44:12
Mono-tasking: causes; treatment going south; nutrients – 1:48:03
Organ VRP locations – 1:50:00
 fail log in
fail log in 2015 London Module 3 Basic
In-clinic strategy & prioritization – 0:00:44
Hypertonic-weak muscles – 0:09:00
Monotasking – 0:10:00
Spinohypothalamic dysfunctions – 0:22:05
Multifidus testing – 0:31:05
Pelvic floor testing – 0:40:13
Adrenals – 0:55:40
 fail log in
fail log in 2016 London Foundation Module 3 (Aug – Dec)
Stim & double stim: tickle, itch, hot, cold and fine touch. – 0:00:48
Vibration: presentation, stim, pacini pairing – 0:05:39
Posture, habits, movement lead-ins to: nociceptors, mechanoreceptors, LKCs – 0:13:46
Pacini vs. Raffini vs. Golgi receptors – 0:21:40
Example of LKC going from pubic symphasis through hyoid to tongue; inhibition patterns as a result of affected hyoid – 0:26:54
Finding Crude Touch secondary if you found Fine touch primary first & visa versa; presentation – 0:36:10
Large number of muscles weak in the clear; nature of PMRF inhibition pattern – 0:50:25
Gradation of PMRF presentation; Pyramidal & Thalamic inhibition patterns – 0:55:20
Receptor pairings – 0:58:14
Adrenals: assessment tests, pairing – 1:01:46
Joint position sense: conscious vs. unconscious, surrogate testing; where to look for golgis; using indicator vs. direct muscle – 1:14:10
LKC priority & assessment – 1:21:58
Approach & strategy in clinic – 1:24:30
Cloacal Synchronization vs. PALO-ALTO; appositional testing – 1:25:38
PALO-ALTO: testing, visual assessment – 1:29:38
 fail log in
fail log in 2015 Sydney Module 3 Basic
Monotasking lead-ins – 0:01:49
Food intolerance – 0:09:35
Rules of receptors – 0:15:13
Cloacals – 0:48:03
Entry points checklist in-clinic – 0:51:54
Adrenals – 0:57:08
VRP areas – 1:17:50
Fine-crude touch rules – 1:25:00
Lead-ins for common receptors – 1:33:30
LKCs – 1:36:42
entry clues to spinohypothalamic, soinomes & spinotectal – 1:42:56
High priority receptors – 1:53:55
 fail log in
fail log in 2016 London Module 3 Basic
Double-stim and pairing of spinomesencephalic – 0:00:23
Monotasking – 0:12:15
Spinomesencephalic, spinohypothalamic, spinotectal – 0:16:19
Tickle & itch, fine & crude touch, hot & cold – 0:28:16
LKCs – 0:43:00
Adrenal fatigue – 0:51:37
Cloacals – 0:53:55
Recurring muscle weakness – 0:55:50
Foundation 4 Day 4
 fail log in
fail log in Sydney Review
 fail log in
fail log in Sydney Foundations Module 4
 fail log in
fail log in 2016 London Foundation Module 4 (Aug-Dec)
Spinotectal dysfunction & finding hidden nociceptors; tips; interaction with neo; effect of anti-stimming nociceptor secondary – 0:00:18
Spino-hypothalamic – 0:07:26
Spino-mesencephalic; how to find the pair – 0:08:34
Spino-mesencephalic vs. emotional dysfunction: TL, questions, priority – 0:14:28
Can emotions pair with other than organ? – 0:18:43
Emotion as secondary – 0:20:10
Emotions example – 0:20:45
Spino-tectal vs. NLP eye position – 0:24:56
Tips on pairing emotions – 0:27:20
Finding priority & relevance of emotion to symptoms – 0:30:46
Emotions & hypertonicity – 0:34:43
Cranial faults with breathing patterns, topped by vibration – 0:35:55
Impact paleo at sutures vs. cranial faults – 0:46:26
TMJ: testing, assessment, golgi & pacini – 0:48:48
Vertebral fixations: bilateral weakness, Lovett reactor – 0:50:42
Cranial fault pairing rules – 0:55:16
Case: all discovered receptors in a fractal; checking for meridians; fixation vs. meridian associated point – 0:56:50
Hypertonicity causing dysfunctions: why are they not top? – 1:05:07
 fail log in
fail log in 2016 London 4 | Phoenix 5 Foundation
Finding Meridian dysfunctions; several ways to find primary and secondary – 0:00:15
How to locate alarm point locations – 0:03:40
Related muscles to Meridians – 0:11:10
Why Meridians sometimes don’t have bilateral weakness – 0:16:00
Finding higher level dysfunctions using rules – 0:17:33
Jaw: muscles of mastication, palpation & assessment, various stims, treatment – 0:21:10
Emotional dysfunctions; multiple ways to determine primary emotion – 0:40:52
Emotions: when organ is primary – 0:53:33
How to determine if Spinomesencephalic is above Emotion – 0:54:27
Review of Psychological reversal – 1:00:12
Cranial Faults: lead-ins, using breath to assess, – 1:03:14
All abdominals, multifidi, spinales, subclavius tests: vectors – 1:22:20
Reasons for bilateral weakness, Spinal Fixations – 1:26:36
 fail log in
fail log in 2015 Sydney Module 4 Basic
Emotions – 0:01:02
Psychological reversal – 0:13:23
Meridians – 0:19:02
Cranial faults & endocrine glands – 0:32:08
Glabella, Sacral cranial faults – 0:33:44
AO Counter-Torque cranial fault – 0:39:33
Coccyx – 0:41:48
Anterior inferior sacral ilio-lumbar ligament; Frozen Gait – 0:46:28
Hyoid – 0:51:20
Neurological tooth – 1:00:38
Joint Position Sense – 1:05:15
Priority – 1:08:20
Tickle-itch dysfunction demo – 1:09:37
Universal Cranial Fault – 1:10:58
TMJ – 1:13:42
 fail log in
fail log in 2015 London Module 4 Basic
Hyoid – 0:01:16
TMJ – 0:09:30
Spinotectal response and uses – 0:24:52
Emotions – 0:36:46
Psychological reversal – 0:51:00
Emotions – 1:05:32
Meridians – 1:12:38
Cranial faults – 1:24:32
Joint capsule golgis – 1:43:14
Primary rules – 1:45:15
Sympathetic/parasympathetic imbalance – 1:47:47
Neurologic tooth – 1:49:20
Jaw protrusion / retraction & near / far focusing – 1:57:30
TS line – 2:02:18
Intermediate 1
 fail log in
fail log in 2018 Vancouver / Poland Intermediate Module 1
Priority
DUTL
Triple Stim
Sequences
Shoulder
Hip
Knee
Aerobic/Anaerobic
 fail log in
fail log in 2016 Oakland Intermediate Module 2
Auditory spinotectal, auditory brain nuclei & auditory receptor dysfunctions: case and differentials – 0:00:30
Priority protocol – 0:12:28
R&R priority check – 0:16:20
Spondylogenic reflexes & TS line – 0:18:26
Flavum ligament – 0:37:12
Aerobic & anaerobic dysfunction, symptoms, nutrients & exercise – 0:40:00
Priority & distortion – 0:44:12
Knee ligaments & orthopedic tests – 0:48:38
Priority with aerobic & anaerobic – 0:58:00
Knee – elbow joint connection – 0:59:43
Ligaments of knee & ankle, interosseous membrane: common pairs, unusual pairings, possible pitfalls – 1:02:40
Stimming golgis at a specific vector – 1:13:00
Testing the three Peroneals – 1:14:01
Pain patterns – 0:15:11
Lateral & medial compression test on knee – 1:15:54
Auditory receptors – 1:21:27
Associated & ancillary hypertonic muscles – 1:24:52
Use of d-UTL – 1:35:09
 fail log in
fail log in 2016 London Intermediate Module 1 (Aug-Dec)
- The fastest way to identify a top priority dysfunction? 0:00:14
- How to triple stim a Joint capsule golgi (eg Pelvic Cat 3)? 0:29:48
- How to know if a LKC is priority? 0:32:26
- How do you triple stim heat receptors? 0:40:23
- How to test a R&R for Priority? 0:41:54
- How to use Sequences in clinic? 0:51:05
- How to use Spondylogenic in clinic? 0:52:05
- How to use DUTL 0:52:50
- Practical uses of ancillary muscles? 1:01:35
- Causes for higher ilium 1:03:10
- Common receptors in clinic 1:04:52
- Several top priorities related to the same trauma 1:06:51
- How to check if muscle is completely cleared from all dysfunctions? 1:08:32
- Spinotectal vs an eye dysfunction 1:14:03
 fail log in
fail log in 2016 Chicago Module 1 Intermediate
Priority for sequence – 0:00:26
Popping, cracking shoulder – 0:01:42
Pain with concentric vs. eccentric movement – 0:03:35
Test for coracobrachialis – 0:04:55
Rub technique for sequences – 0:05:55
Priority for sequence – 0:11:40
Ligament vs. muscle sequence – 0:17:50
Humeral depression – 0:25:44
Normal motion/rhythm of the humerus, scapula & clavicle – 0:26:38
Sequences & long-lasting UTL – 0:30:48
Visual assessment of sequences – 0:32:25
Shoulder assessment & case: popping, clicking & floaty clavicle – 0:34:30
Clavicle vs. shoulder abduction sequence – 1:01:24
Muscle testing tips – 1:06:45
Hypertonicity: associated or ancillary muscle – 1:08:18
Receptors in bursa – 1:15:08
Humeral depressors case – 1:25:03
Neurologic tooth – 1:31:02
 fail log in
fail log in 2016 Chicago Module 2 Intermediate
Rules: 2 secondaries of the same fractal – 0:00:51
Hypertonic muscles & modes of dysfunction – 0:03:12
Long lasting UTL vs. d-UTL – 0:04:13
Ligament vs. muscle sequence – 0:08:51
Full review of ligaments of the knee, common pairings. – 0:11:48
Knee miniscus passive & active movement – 0:26:17
Ligaments of the hip – 0:31:21
Ligaments of the ankle – 0:36:27
Orthopedic tests for hip & knee; muscle tests – 0:40:53
Muscle tests for the various hamstring muscles & heads – 0:44:46
Movements of the knee, screw-home mechanism – 0:48:25
Condyle movement & mechanics – 0:52:15
Ligaments of medial and lateral knee rotation – 0:54:48
Knee pathologies with step-up test – 0:57:08
Bifurcate ligament in the ankle – 1:04:45
Screw-home mechanism – 1:08:38
Patient that can’t do ground splits: real-time treatment – 1:10:03
Proper angle of anteversion of hip – 1:18:34
Aerobic & anaerobic testing – 1:24:06
Concussion case – 1:35:06
 fail log in
fail log in 2016 Oakland Module 1 Intermediate
Determining priority with uncommon receptors – 0:00:31
Sequences – 0:25:12
Hypertonicity – 0:31:45
Reactor-reactive (R&R) priority – 0:35:00
Ligaments of the shoulder – 0:38:35
Meridians priority – 0:44:05
Clavicle movement rhythm – 0:45:13
Priority: joint position vs. sequnce – 0:46:25
Glitches in triple stim – 0:56:30
links between fractals of different time periods – 1:01:28
Shoulder assessment & case – 1:03:25
Priority rules – 1:32:56
Joint Position Sense vs. Sequence – 1:38:32
Hypertonicity – 1:43:57
Joint Position Sense vs. Sequence – 1:47:43
Intermediate 2
 fail log in
fail log in TMJ & Facial Ligament Tutorial
 fail log in
fail log in Sydney Intermediate Review
Review of module 1 and pre-information for module 2
 fail log in
fail log in 2018 Vancouver Intermediate – Supplemental
1:27 – Using DUTL to map a fractal
27:45 – Assessing problems with gliding of humeral head
31:06 – Importance of testing hip in extension
32:13 – FHL and it’s importance to the talus
34:10 – Tarsal tunnel syndrome & Morton’s neuroma
35:08 – Plantar fasciitis – causes and treatment approaches
35:50 – Traction indications & contraindications for spinal disc injury
39:15 – Assessing problems with vertebral gliding
48:25 – Iliolumbar ligament testing
51:20 – Apical ligament of the dens
53:00 – Coupled motion assessment and treatment
57:00 – Short Axial Ligament
1:03:30 – Hypertonicity: Associated or Ancillary
 fail log in
fail log in 2017 London : Australia Intermediate Module 2
Muscle referred pain, d-UTL & Priority: case of top impact paleo & mapping a variety of receptors in below it; hypertonicity & d-UTL – 0:03:14
Bullet-proofing work: using functional vs. dysfunctional spinotectal; distringuishing with cerebellar and cranial nerve dysfunctions – 0:36:14
Golgis around the eyes – 0:48:08
Triggers, returning dysfunctions – 0:49:30
Challenging the corrections – 1:03:02
Rules of hypertonicity: differentiating between hypertonic & weak vs. hypertonic & strong – 1:04:18
Aerobic / anaerobic dysfunction & d-UTL – 1:06:14
Top dysfunction & hypertonicity – 1:16:25
Tickle & itch stim, d-stim & triple-stim – 1:17:08
Elbow & knee coupling; short LKCs – 1:19:00
Ligaments & sequences of hip & knee; meniscus; ACL-PCL pairing – 1:23:33
Pelvic floor & hypertonicity – 1:36:08
VRP stimulation – 1:38:43
 fail log in
fail log in 2016 Oakland Intermediate Module 3
Spinal coupling: protocol & priority – 0:00:20
Upper cervical coupling; local receptor switching – 0:14:40
Feeling worse after session: post-session reorganization – 0:43:00
Homework assignments – 0:46:47
Diaphragm recap – 0:49:36
Spinal glide vs. iliolumbar ligament dysfunction – 0:55:36
Ligament rules & muscle inhibition of hips ligaments – 1:06:58
Sequences: spine, hips – 1:11:16
Assessing cervical spine motion & ligaments; apical, atlanto-axial; Luschka joints; TS line – 1:19:20
Cervical ligament vs. eye vs. brain nuclei dysfunctions – 1:35:50
Master Class
 fail log in
fail log in 2017 PV Master Class
D-UTL with Joint Position Sense and non-priority receptor – 0:00:58
Pulls / pools – 0:12:45
Basal ganglia – 0:17:50
D-UTL with aerobic / anaerobic dysfunction – 0:30:00
Tremors & basal ganglia – 0:39:20
D-UTL and spinal coupling – 0:40:27
D-UTL and hard-ti-test muscles: pelvic floor & jaw – 0:41:47
Teeth & face VRPs – 0:44:45
Testing with sugar on gums – 0:59:55
Facial ligaments – 1:13:50
Food intolerance using d-UTL – 1:21:16
Surrogate Testing – 1:30:38
Brain nuclei sequence – 1:37:09
Sydney Advanced I Web Class
 fail log in
fail log in Sydney Advanced I Web Class
Advanced I
Tongue
Organs
Baroreceptors

